Lenzilumab Treatment Response in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Correlates with C-Reactive Protein Levels
- Multi-variate analysis of LIVE-AIR Phase 3 data demonstrates that elevated baseline C-Reactive Protein (“CRP”) is the most predictive feature for progression to invasive mechanical ventilation (“IMV”) or death and may be a useful biomarker to guide therapeutic intervention
- Patients with baseline CRP<150 mg/L who received lenzilumab had a more than 2.5-fold higher likelihood to survive without IMV than patients who received placebo (p<0.001)
- Findings suggest hospitalized COVID-19 patients who are early in the hyper-immune response, with lower baseline CRP levels (CRP<150 mg/l), achieve even greater clinical benefit from lenzilumab treatment
Excerpt from the Press Release:
BURLINGAME, Calif.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Humanigen, Inc. (Nasdaq:HGEN) (“Humanigen”), a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on preventing and treating an immune hyper-response called ‘cytokine storm’ with its lead drug candidate, lenzilumab, announced that a manuscript detailing the results of an analysis of CRP levels from the LIVE-AIR Phase 3 study is available on medRxiv (https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.30.21267140v1) . The results indicate the greatest clinical benefit of lenzilumab treatment may be achieved in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with lower baseline CRP levels, which typically occur earlier in the progression of the disease.
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is an early upstream mediator and orchestrator of the hyperinflammatory immune response following SARS-CoV-2 infection and serves to activate and expand inflammatory myeloid cells. Increases in CRP are driven by elevations of myeloid cell derived downstream cytokines. Highly elevated levels of CRP (>150 mg/L) may indicate a stage of the hyperinflammatory immune response by which sufficient myeloid activation has already occurred, rendering GM-CSF neutralization less adequate to prevent further disease progression.
This analysis and publication provide evidence that a biomarker-driven approach utilizing baseline CRP levels to guide therapeutic intervention and patient selection may improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“We are encouraged by these results” said Dr. Dale Chappell, Chief Scientific Officer, Humanigen. “In the context of other GM-CSF targeting therapies having failed to progress in development for COVID-19, these results confirm the importance of patient selection and understanding disease processes when designing clinical trials. Importantly, ACTIV-5/BET-B, a potentially confirmatory Phase 2/3 study, utilizes CRP<150 mg/L to define the primary analysis population.”
Dr. Cameron Durrant, Chief Executive Officer, Humanigen, added, “The PREACH-M study in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia being conducted at 5 centers in Australia has begun dosing patients. Both the SHIELD study in CAR-T and the RATinG study in acute Graft versus Host Disease (aGvHD) are planned to begin enrolling in the first half of 2022, in the US and the UK respectively. Additional COVID studies which will be completed or initiated in 2022 include the NIH-sponsored ACTIV-5/BET-B study in the US and Korea and the C-SMART study being conducted in Australia. All are late-stage, clinical studies. Further strengthening the Humanigen pipeline is our Phase 1 program focused on ifabotuzumab in solid tumors.”
About the LIVE-AIR, Phase 3 Study of Lenzilumab
This study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center Phase 3 trial for the treatment and prevention of serious and potentially fatal outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia. The primary objective was to assess whether lenzilumab, in addition to other treatments, which included dexamethasone (or other steroids) and/or remdesivir, could prevent or alleviate the immune-mediated ‘cytokine storm’ and improve survival without ventilation, or ‘SWOV’ (sometimes referred to as ‘ventilator-free survival’). SWOV is a composite endpoint of time to death and time to invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) and SWOV is an important clinical endpoint that measures not only mortality, but the morbidity associated with mechanical ventilation. Approximately 94% of patients received dexamethasone (or other steroids), 72% received remdesivir, and 69% received both.
Click the button below to read the entire Press Release:
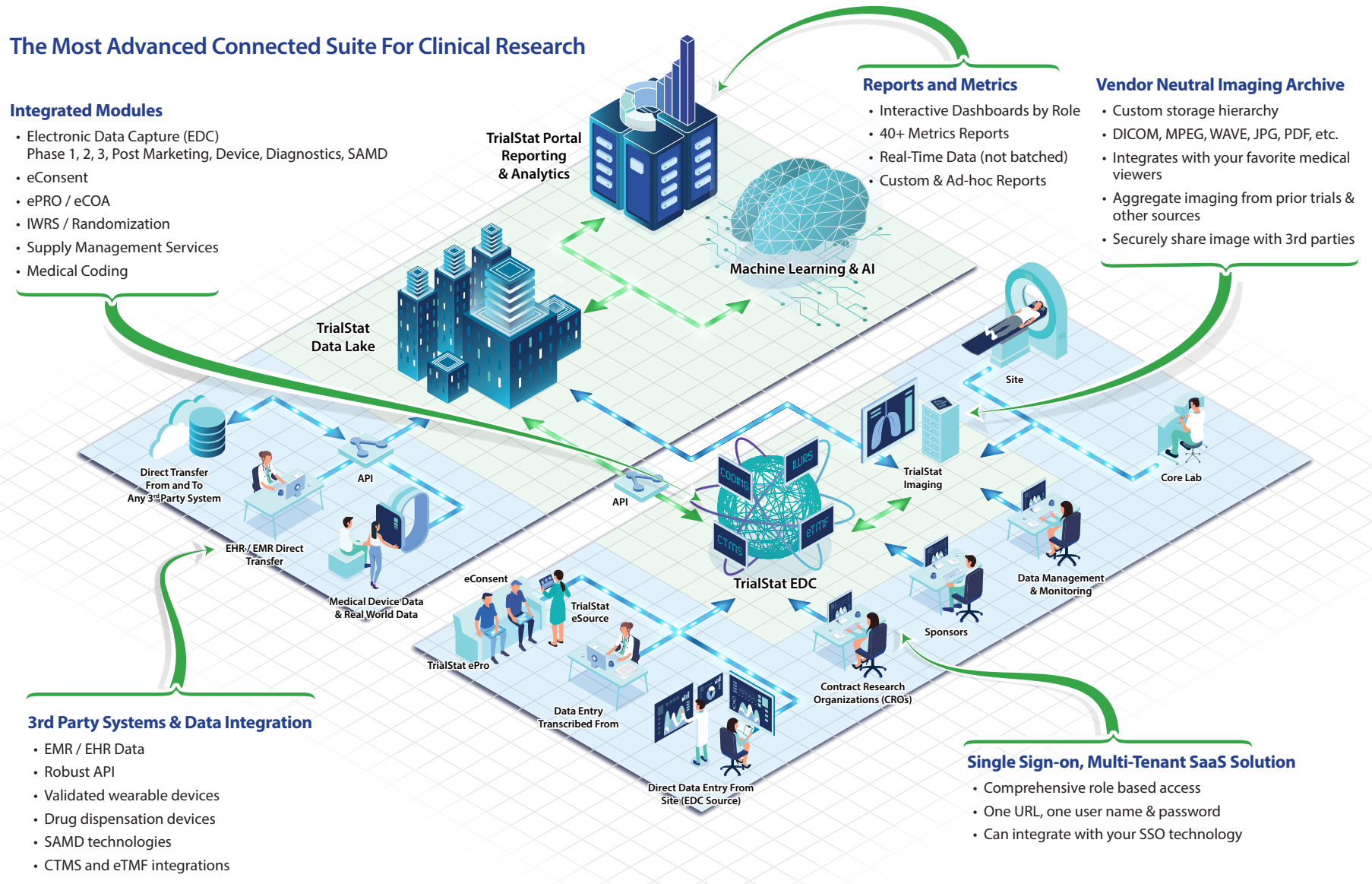
Discover What Sets TrialStat Apart From Ordinary EDC Platforms
Click the image or button below to explore our eClinical Suite Platform and discover what sets TrialStat apart from competing EDC platforms.
Request Your Demo Today!
From rapid database build through database lock, we deliver consistent quality on-time and on-budget. Ready to upgrade your eClinical toolkit?