CHOP-led Research Study Identifies Key Target in Treatment-Resistant Hemophilia A
Excerpt from the Press Release:
PHILADELPHIA, April 15, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have identified a key target that may be responsible for treatment failure in about 30% of patients with hemophilia A. The target, known as B cell activating factor (BAFF), appears to promote antibodies against and inhibitors of the missing blood clotting factor that is given to these patients to control their bleeding episodes. The findings, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, raise the possibility of using anti-BAFF therapies, potentially in combination with immune tolerance therapies, to tame the immune response in some patients with severe hemophilia A.
Hemophilia A is the most common inherited bleeding disorder, affecting 1 in 10,000 men worldwide. The condition is the result of a missing coagulation factor known as factor VIII (FVIII), which leads to uncontrolled bleeding episodes, joint disease, and increased risk of death. To control the disease, patients receive infusions of the FVIII protein to replace the missing coagulation factor, but for reasons scientists haven’t fully understood, approximately 30% of patients with severe hemophilia A develop neutralizing antibodies known as FVIII inhibitors that prevent the treatment from working, which negatively affects disease management.
Click the button below to read the entire Press Release:
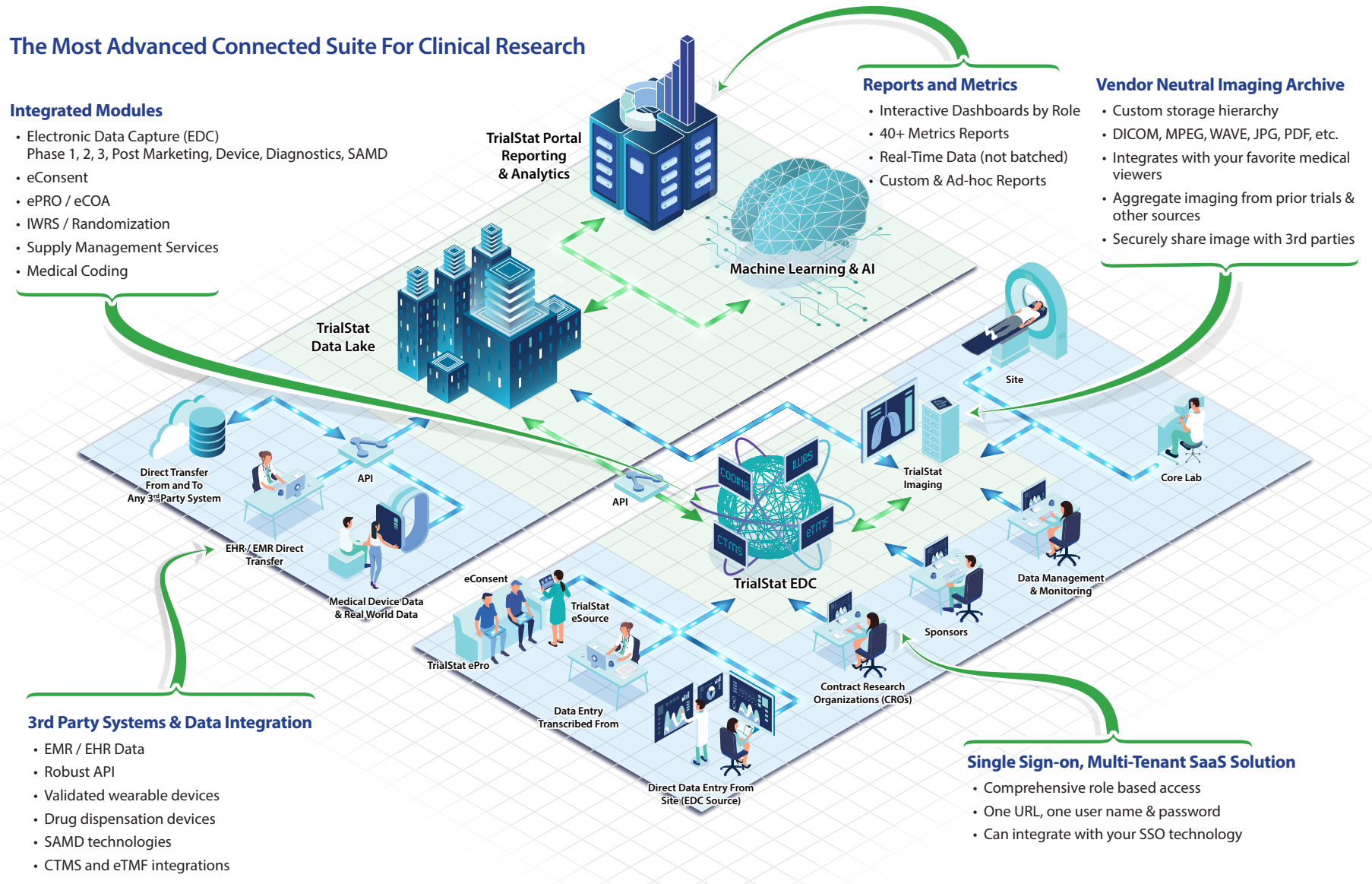
Discover What Sets TrialStat Apart From Ordinary EDC Platforms
Click the image or button below to explore our eClinical Suite Platform and discover what sets TrialStat apart from competing EDC platforms.
Request Your Demo Today!
From rapid database build through database lock, we deliver consistent quality on-time and on-budget. Ready to upgrade your eClinical toolkit?