ASLAN Pharmaceuticals Presents Late-Breaking Poster on Eblasakimab and Neuronal Itch Mechanisms at the 2022 Society for Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting
Excerpt from the Press Release:
MENLO PARK, Calif. and SINGAPORE, May 20, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — ASLAN Pharmaceuticals (Nasdaq: ASLN), a clinical-stage, immunology-focused biopharmaceutical company developing innovative treatments to transform the lives of patients, today announced the presentation of a poster highlighting new data and insights related to neuronal itch mechanisms through eblasakimab’s targeting of IL-13Rα1 at the Society for Investigative Dermatology (SID) Annual Meeting. The data were presented by Ferda Cevikbas PhD, Head of Translational Sciences at ASLAN.
Chronic itch is a hallmark and major symptom of atopic dermatitis and other tType 2-driven inflammatory skin disorders. Itch signaling in atopic dermatitis (AD) has been recently postulated to be exacerbated by pro-inflammatory cytokines present in the skin1, causing an immune response that disrupts the skin barrier and drives disease pathology. In our study, we show that IL-13 and IL-4 act as neuronal enhancers for the amplification of itch pathways through the IL-13Rα1 subunit of the Type-2 receptor and these effects can be inhibited by eblasakimab.
Dr Alexandre Khaoukhov, Chief Medical Officer, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, commented: “Aside from the painful, inflamed skin lesions seen in patients with atopic dermatitis, chronic itch can be a debilitating addition to the overall burden of this disease, significantly impairing quality of life. These data paint an encouraging picture of eblasakimab’s role in reducing pruritic neuronal responses and add to our understanding of the benefits of eblasakimab’s unique mechanism of action in its dual blockade of both IL-4 and IL-13 through the Type 2 receptor.”
Publication details
The poster titled, “New insights into neuronal itch mechanisms by targeting IL-13Rα1 with eblasakimab” presents results from an ex vivo study in human dorsal root ganglia (hDRG) neurons after being pre-treated with eblasakimab, IL-4 alone, IL-13 alone or a combination of both IL-4 and IL-13. Neuronal responses were captured by live cell calcium imaging.
Eblasakimab significantly reduced cytokine-enhanced neuronal responses to IL-4 and IL-13-driven itch by more than 40% versus control conditions (p=0.0001)2, suggesting eblasakimab’s unique mechanism of blocking IL-13Rα1 could provide a molecular basis for the significant reduction of pruritis scores observed in eblasakimab-treated moderate-to-severe AD patients in the Phase 1b clinical trial.
Click the button below to read the entire Press Release:
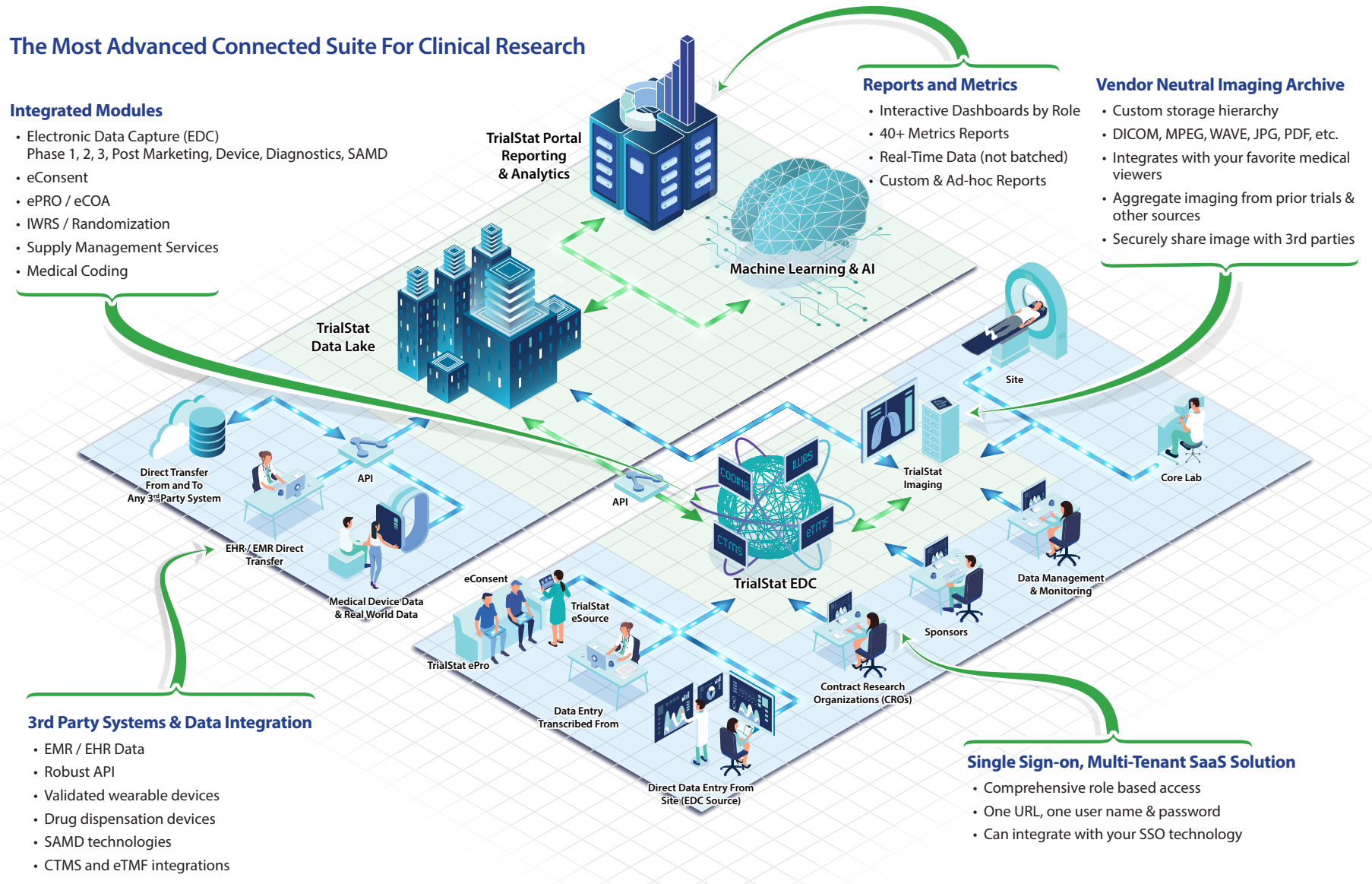
Discover What Sets TrialStat Apart From Ordinary EDC Platforms
Click the image or button below to explore our eClinical Suite Platform and discover what sets TrialStat apart from competing EDC platforms.
Request Your Demo Today!
From rapid database build through database lock, we deliver consistent quality on-time and on-budget. Ready to upgrade your eClinical toolkit?