GRAIL CCGA Discovery Results Published in Cancer Cell Reveal Methylation as Promising DNA Hallmark for Multi-Cancer Early Detection
Methylation Approach Had One of the Highest Cancer Signal Detection Sensitivities and Best Predicted Cancer Signal Origin of the Evaluated Technologies
Approach Informed Development of Galleri® Multi-Cancer Early Detection Blood Test
Analysis is Part of Extensive and Systematic Comparison of Cancer Specific Cell-Free DNA Features for Multi-Cancer Early Detection
Excerpt from the Press Release:
MENLO PARK, Calif.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–GRAIL, LLC, a healthcare company whose mission is to detect cancer early when it can be cured, today announced findings from a fundamental substudy of the Circulating Cell-free Genome Atlas (CCGA; NCT02889978) study, demonstrating that methylation had the most promising combination of cancer detection and prediction of cancer signal origin when compared with other evaluated approaches. This is the first rigorous and systematic comparison of various genomic measures from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for multi-cancer early detection (MCED) testing, and the largest comprehensive genome-wide comparison of cfDNA approaches. Findings were published online in Cancer Cell in a manuscript titled “Evaluation of Cell-Free DNA Approaches for Multi-Cancer Early Detection.”
“Results from the CCGA study formed the basis for how we developed and refined the Galleri test—it’s our origin story and the foundation of our work to transform cancer care with a simple blood test,” said Amoolya Singh, Ph.D., Senior Vice President of Data Science and Chief Scientific Officer at GRAIL. “This defining study made it possible to carefully design a population screening test with a high specificity and low false-positive rate for cancer detection. When combined with standard screenings, this test has the potential to improve detection of cancer in asymptomatic individuals.”
The CCGA Discovery Substudy, the first of three pre-planned substudies of the case-controlled CCGA study, evaluated multiple potential approaches to blood-based multi-cancer early detection (MCED) in a cohort of 2,800 individuals. These approaches included whole-genome sequencing, whole-genome methylation sequencing, and ultra deep targeted sequencing. Together this covered eight classifiers including methylation, somatic copy number alterations, somatic mutations, and a ninth pan-feature classifier. Criteria for evaluation included sensitivity (a test’s ability to correctly identify people with cancer) at high (98%) specificity (a test’s ability to correctly identify people without cancer) and cancer signal origin prediction (a test’s ability to predict the anatomical localization or cell of origin of the detected cancer signal).
Click the button below to read the entire Press Release:
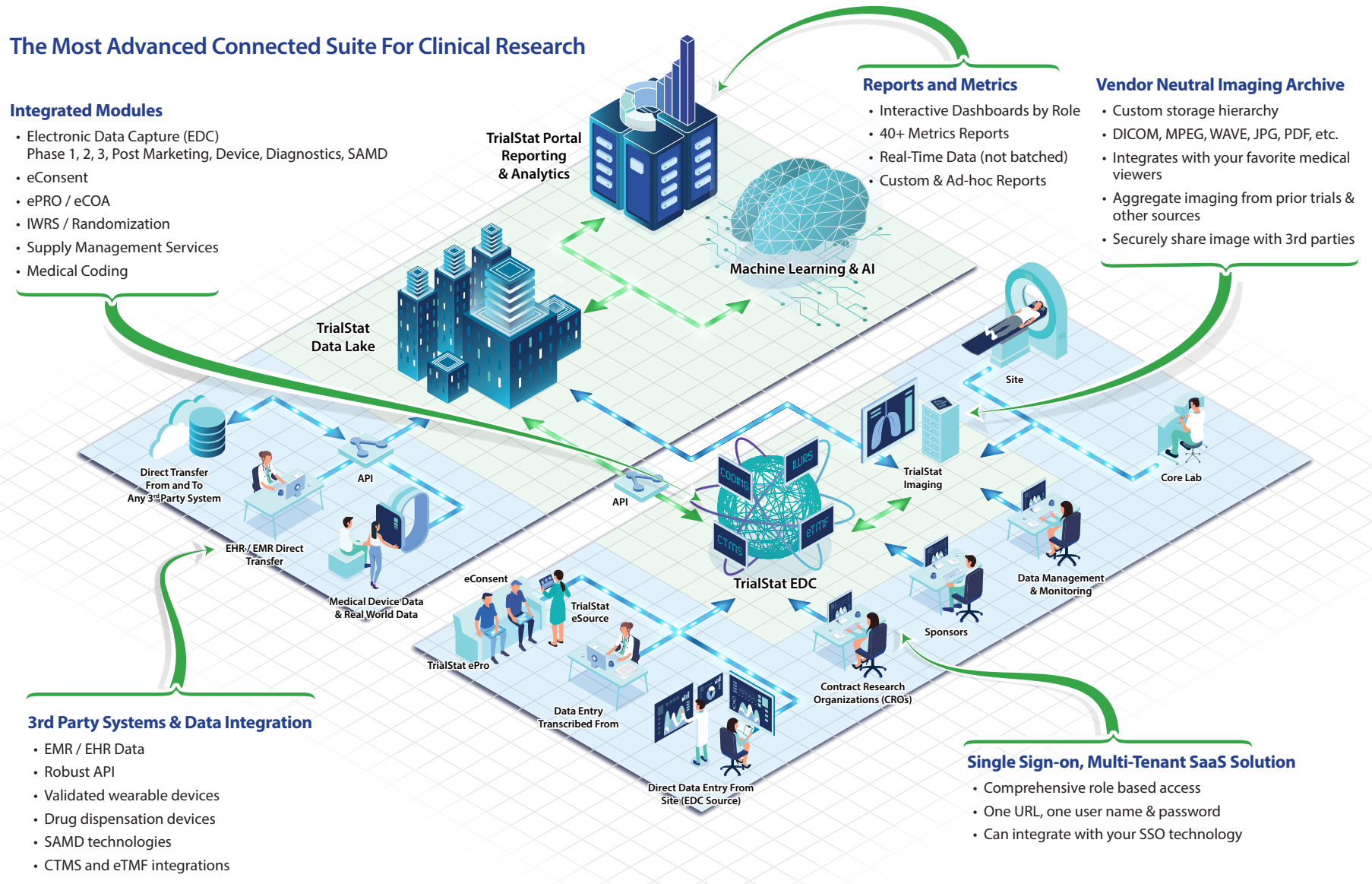
Discover What Sets TrialStat Apart From Ordinary EDC Platforms
Click the image or button below to explore our eClinical Suite Platform and discover what sets TrialStat apart from competing EDC platforms.
Request Your Demo Today!
From rapid database build through database lock, we deliver consistent quality on-time and on-budget. Ready to upgrade your eClinical toolkit?